Introduction
Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending has revolutionized the way people borrow and lend money. It has provided an alternative to traditional banking systems, allowing individuals to directly connect with borrowers or lenders through online platforms. In this article, we will explore the concept of P2P lending, how it works, and its benefits and risks.
Section 1: Understanding P2P Lending
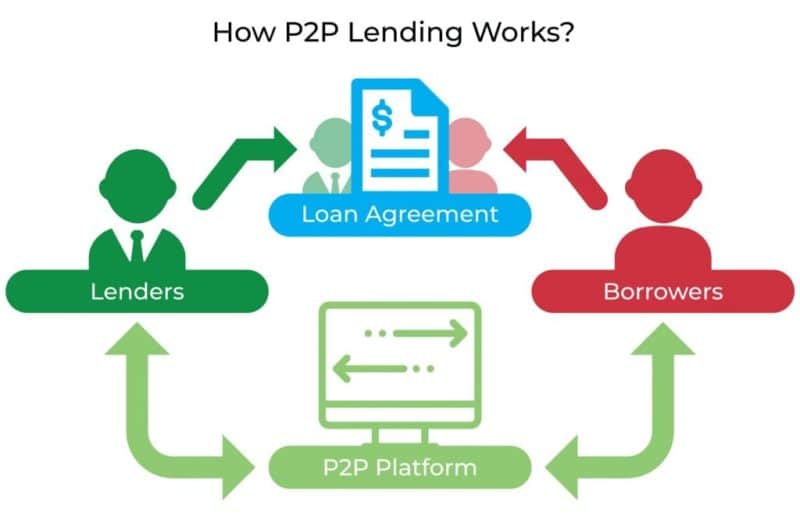
Subsection 1.1: Definition of P2P Lending
P2P lending, also known as marketplace lending, is a form of lending that matches borrowers directly with lenders through online platforms. These platforms act as intermediaries, facilitating the borrowing and lending process. P2P lending eliminates the need for traditional financial institutions, such as banks, by connecting individuals who want to borrow money with those who want to lend money.
Subsection 1.2: The History of P2P Lending
P2P lending originated in the early 2000s when the internet made it possible for individuals to connect and transact directly with each other. The first P2P lending platforms, such as Zopa and Prosper, were established during this time. Since then, P2P lending has experienced significant growth and popularity, with new platforms emerging regularly.
Subsection 1.3: How P2P Lending Differs from Traditional Lending
P2P lending differs from traditional lending in several ways. In traditional lending, banks and financial institutions act as intermediaries, assessing borrowers’ creditworthiness and setting interest rates. P2P lending cuts out these intermediaries, allowing borrowers and lenders to negotiate terms directly. This can result in lower interest rates for borrowers and higher returns for lenders.
Section 2: How P2P Lending Works

Subsection 2.1: The Borrowing Process
To borrow money through a P2P lending platform, borrowers need to create an account and provide information about their financial situation, credit history, and the purpose of the loan. The platform then assesses the borrower’s creditworthiness and assigns them a risk rating. Based on this rating, the borrower is assigned an interest rate, which can vary depending on their creditworthiness.
Subsection 2.2: The Lending Process
Lenders on P2P lending platforms can browse through loan listings and choose which loans to fund. They can diversify their investments by lending small amounts to multiple borrowers, spreading the risk. Lenders can also set their desired interest rates and choose the duration of their loans. Once the loan is funded, borrowers receive the requested amount, and lenders start earning interest on their investment.
Subsection 2.3: Loan Repayment and Default
Borrowers repay their loans through monthly installments, including both principal and interest. P2P lending platforms typically handle the collection and distribution of payments. In case of default, the platform may have a collection process in place, including legal actions if necessary. However, P2P lending carries a higher risk of default compared to traditional lending, as borrowers may have lower credit scores or face financial difficulties.
Section 3: Benefits and Risks of P2P Lending
Subsection 3.1: Benefits of P2P Lending
- Higher Returns for Lenders: P2P lending offers potentially higher returns compared to traditional savings accounts or other low-risk investments.
- Lower Interest Rates for Borrowers: Borrowers may get access to lower interest rates compared to traditional loans, especially if they have a good credit history.
- Flexible Terms: P2P lending allows borrowers and lenders to negotiate terms directly, offering more flexibility compared to traditional lending.
Subsection 3.2: Risks of P2P Lending
- Default Risk: P2P lending carries a higher risk of default compared to traditional lending, as borrowers may have lower credit scores or face financial difficulties.
- Platform Risk: The success and stability of a P2P lending platform are crucial for both borrowers and lenders. If a platform fails, it may affect the repayment process and the investors’ ability to recover their funds.
- Lack of Regulation: P2P lending is a relatively new industry, and regulations may vary across jurisdictions. This lack of regulation can expose borrowers and lenders to potential risks.
Section 4: Tips for Borrowers and Lenders
Subsection 4.1: Tips for Borrowers
- Check Your Credit Score: Before applying for a loan, check your credit score and work on improving it if necessary.
- Compare Interest Rates: Compare interest rates and terms offered by different P2P lending platforms to find the best deal.
- Borrow Responsibly: Only borrow what you can afford to repay, considering both the interest payments and your monthly budget.
Subsection 4.2: Tips for Lenders
- Diversify Your Investments: Spread your investments across multiple loans to reduce the risk of default.
- Research Borrowers: Take the time to review borrowers’ profiles, credit history, and purpose of the loan before investing.
- Monitor Your Investments: Regularly monitor the performance of your loans and reinvest your returns to maximize your earnings.
Conclusion
P2P lending has democratized the lending and borrowing process, providing individuals with an alternative to traditional banking systems. While it offers benefits such as higher returns for lenders and lower interest rates for borrowers, it also carries risks, including default risk and platform risk. By understanding how P2P lending works and considering the associated risks and benefits, borrowers and lenders can make informed decisions and participate in this growing industry.
